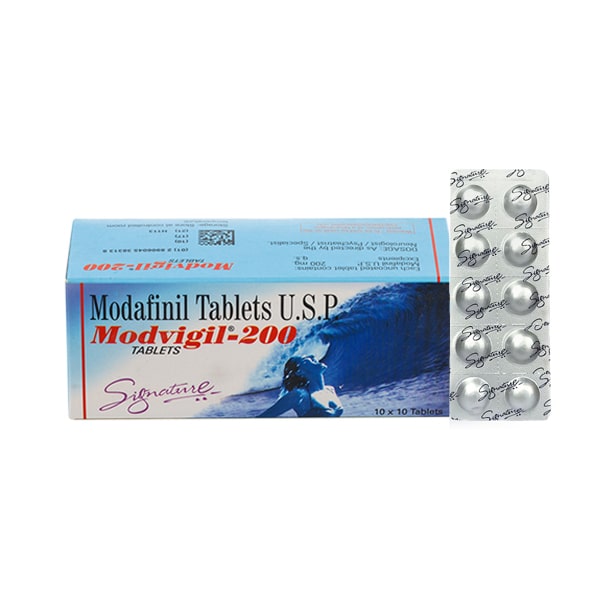
Pharmacological Profile: Modafinil (Modvigil) – This is being shipped directly from our US Domestic warehouse, arriving at your doorstep quickly and safely.
Overview and Mechanism of Action
Modafinil is a unique eugeroic (wakefulness-promoting) agent that differs chemically and pharmacologically from classical sympathomimetic stimulants like amphetamines. While its precise mechanism remains a subject of ongoing research, it is primarily identified as an atypical dopamine transporter ($DAT$) inhibitor. By binding to the $DAT$ with relatively low affinity, it increases extracellular dopamine concentrations in the synaptic cleft. Additionally, it is hypothesized to modulate the hypothalamic orexin/hypocretin and histamine systems, which are critical for the regulation of arousal and the sleep-wake cycle.
Clinical Applications
- Promotion of Wakefulness: Indicated for the management of excessive daytime sleepiness ($EDS$) associated with narcolepsy and obstructive sleep apnea ($OSA$).
- Circadian Rhythm Regulation: Utilized in the treatment of Shift Work Disorder ($SWD$) to maintain alertness during nocturnal periods.
- Cognitive and Neuroprotective Research: Frequently studied in academic contexts for its potential pro-cognitive effects and its role in increasing neuronal activation in discrete regions of the hypothalamus.
Administration Protocols
- Bioavailability: Rapidly absorbed following oral administration, achieving peak plasma concentration ($C_{max}$) within 2 to 4 hours.
- Dosing Constraints: Typically administered as a single daily dose (200 mg). Due to its long elimination half-life (12–15 hours), frequent dosing is unnecessary and may lead to sleep onset latency issues.
- Metabolic Considerations: Metabolized primarily by the liver via amide hydrolysis and cytochrome P450 (specifically $CYP3A4/5$). While food does not significantly impact overall bioavailability, it may delay $T_{max}$ by approximately one hour.
Adverse Reactions and Safety Profile
- Common Clinical Observations: Cephalalgia (reported in ~34% of patients), nausea, and xerostomia (dry mouth).
- Neurological and Psychiatric Effects: Frequent reports of anxiety, nervousness, and insomnia. Unlike traditional stimulants, it exhibits a lower propensity for peripheral sympathomimetic effects like tachycardia.
- Severe Dermatological Risks: Although rare, modafinil has been associated with serious cutaneous reactions, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome ($SJS$) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis ($TEN$), necessitating immediate cessation upon the appearance of a rash.